- About Us
- Partnerships
- Product Portfolio
- Investors
- Patients
- Physicians
- CSR
- Press & Media
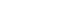


WHAT IS OVARIAN CANCER?
Ovarian cancer is a disease in which normal cells in an ovary change, grow uncontrollably, and form a mass of cells called a tumor. Epithelial carcinoma, which begins in cells on the outer surface of the ovary, is the most common type of ovarian cancer.
WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF THE OVARIES?
Every woman has two ovaries, the almond-shaped glands that contain the eggs. During ovulation, an egg is released from an ovary and travels to the uterus through the fallopian tube. The ovaries are the primary source of estrogen and progesterone, the hormones that inf luence breast growth, body shape, and body hair, and regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS:
Ovarian cancer was once thought to cause no symptoms. However, recent studies have shown that woman with ovarian cancer are more likely to have the following symptoms or signs, even if the cancer is in an early stage. Sometimes, women with ovarian cancer do not show any of these symptoms. Or, these symptoms may be caused by a medical condition that is not cancer.
For many women with ovarian cancer, these symptoms occur often and are different from what is normal for their bodies. Women who have these symptoms almost daily for more than a few weeks should see a gynecologist (a doctor who specializes in treating diseases of the female reproductive organs). Early medical evaluation may help detect the cancer at the earliest possible stage of the disease, when it is easier to treat.
Women with ovarian cancer may also have the following symptoms:
However, these symptoms are equally as likely to be caused by another medical condition. If you are concerned about any of these symptoms or signs, please talk with your doctor.
DIAGNOSIS
Doctors use many tests to diagnose cancer and find out if it has metastasized (spread). Some tests may also determine which treatments may be the most effective. For most types of cancer, a biopsy is the only way to make a definitive diagnosis of cancer. If a biopsy is not possible, the doctor may suggest other tests that will help make a diagnosis. Imaging tests may be used to find out whether the cancer has metastasized
As with all cancers, early detection and treatment is important. However, early detection of ovarian cancer is difficult. Often, women don’t have any symptoms until the later stages of the disease. In fact, 70% of ovarian cancers are not found until the disease is in an advanced stage and has spread to other parts of the body, most commonly the abdomen.
In addition to a physical exam, the following tests may be used to diagnose ovarian cancer:
PELVIC EXAMINATION:
Transvaginal ultrasound
CA-125 ASSAY: This blood test measures a substance called CA-125, a tumor marker, which is found in higher levels in women with ovarian cancer. Woman younger than 50 with conditions such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and uterine fibroids may have an increased CA-125 level. This test is more accurate in postmenopausal women.
Biopsy.A biopsy is the removal of a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope
X-RAY: An x-ray is a picture of the inside of the body. For instance, a chest x-ray can show if the cancer has spread to the lungs.
LOWER GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) SERIES: This is a series of x-rays of the colon and rectum taken after the patient has a barium enema. The barium highlights the colon and rectum on the x-ray, making it easier to identify a tumor or abnormal area in those organs.
Computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan.
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan.
WHAT DOES STAGE MEAN?
The stage is a way of describing a cancer, such as where it is located, if or where it has spread, and whether it is affecting the functions of other organs in the body. There are four stages for ovarian cancer: stages I through IV (one through four). Details about these stages are available at www.cancer.net/ovarian
HOW IS OVARIAN CANCER TREATED?
The treatment of ovarian cancer depends on the size and location of the tumor, whether the cancer has spread, and the woman’s overall health. Surgery is often the first treatment and may include the removal of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus. Chemotherapy may be given to lower the risk of cancer returning and/or treat metastatic cancer. Radiation therapy is not often used to treat ovarian cancer but may be used to relieve side effects. When making treatment decisions, women may also consider a clinical trial; talk with your doctor about all treatment options. The side effects of ovarian cancer treatment can often be prevented or managed with the help of your health care team.